

The result was "an electrical island in the United States," Bill Magness, CEO of ERCOT, said. Cudahy wrote in a 1995 article, "The Second Battle of the Alamo: The Midnight Connection.” "This policy of isolation avoided regulation by the newly created Federal Power Commission, whose jurisdiction was limited to utilities operating in interstate commerce." "By eschewing transmission across state lines, the Texas utilities retained freedom," Richard D. "Utilities in Texas were smart and made an agreement that no one was going to extend power outside of Texas," Donna Nelson, who served as chair of the state Public Utility Commission, which oversees ERCOT, from 2008 to 2017, said in an ERCOT promotional video about the history of the grid.
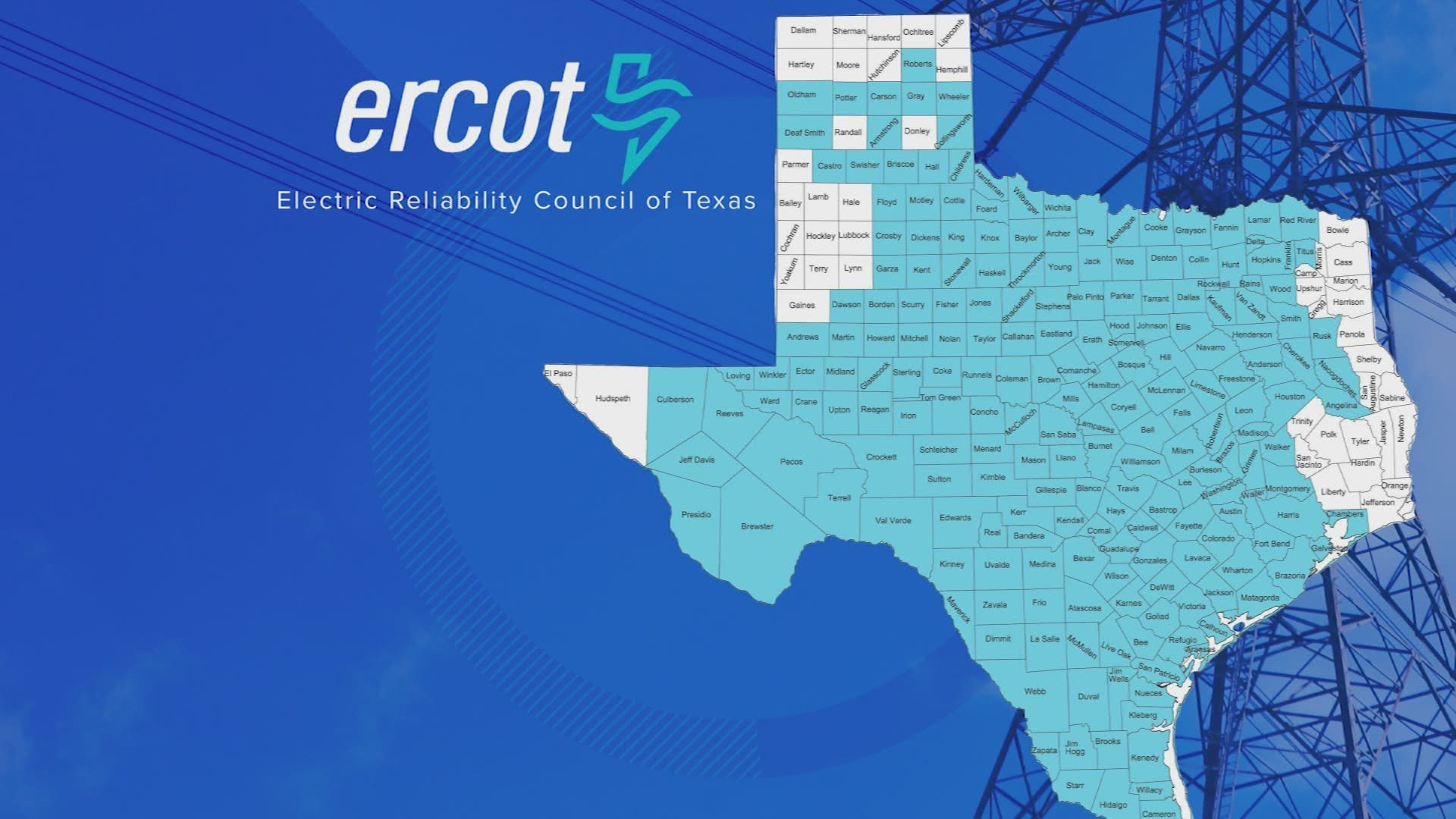
More: More than 100 insurance companies sue ERCOT over claims related to February 2021 freeze Power breakdown: What percentage of Texas energy is renewable? Detailing the state's power sources from gas to wind. Roosevelt signed the Federal Power Act, which charged the Federal Power Commission with regulating interstate electricity sales. The predecessor for ERCOT was formed in the 1930s, after President Franklin D. The reasons Texas controls its own grid, journalist Kate Galbraith observed in a Texplainer piece for the Texas Tribune in 2011, have to do with the same theme that colors so much of Texas' history and public policy: a distrust of federal interference. The country is divided into three grids: one covers the eastern U.S., another the western states and then there is the Texas grid, which covers nearly the entire state. As winter storm blackouts roiled Texas in early 2021, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas, the nonprofit that operates Texas' electrical grid, gained notoriety - as well as the simple fact that Texas has its own electrical grid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
